The turbo, or turbine, is a key component of modern engines, and is responsible for a significant increase in performance and efficiency. In this article, we will explore in detail what a turbocharger is, how it works and how it has revolutionised the automotive industry.
Introduction to Turbo
The turbo, short for 'turbocharger,' is a device found in the fuel system of an engine. Its main function is to increase the amount of air entering the engine's cylinders. An increased flow of air enables better combustion of fuel, which results in increased engine power and torque.
The Basic Structure of the Turbo
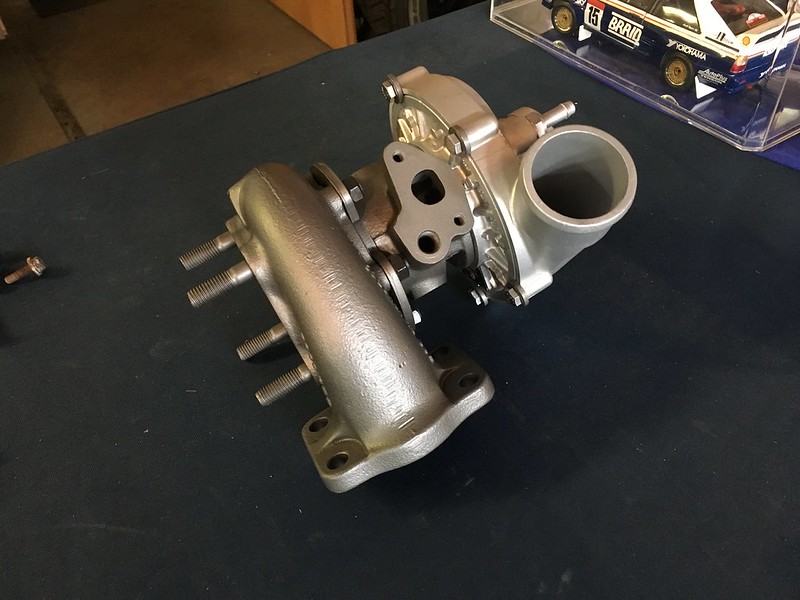
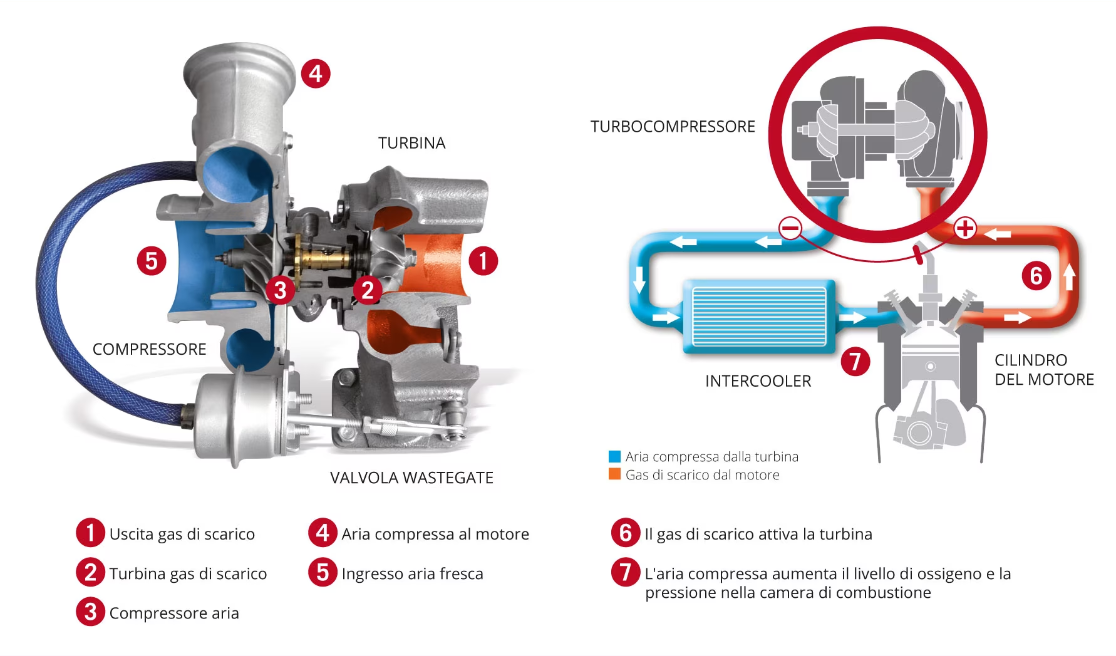
A turbocharger consists mainly of two main components: the turbine and the compressor. Both consist of impellers equipped with vanes and are connected to each other by a shaft.
-
Turbine: The turbine is located in the engine's exhaust system and consists of a scroll. When the exhaust gases are directed towards the turbine, it starts to turn.
-
Compressor: The compressor is located in the air intake system. The rotation of the turbine sets the compressor in motion, which draws in air and compresses it before it enters the engine cylinders.
How Turbo Works
Turbo operation is closely linked to the turbocharging principle. Exhaust gases escaping from the engine's combustion chamber are directed towards the turbine. When these gases hit the turbine blades, they make the turbine turn at high speed.
This rotation of the turbine is mechanically connected to the compressor. The compressor, in turn, begins to draw in air from outside and compresses it. The compressed air passes through a radiator known as an intercooler, where it is cooled to increase its density.
After passing through the intercooler, the compressed air is directed into the engine's intake ducts. This increase in air pressure allows more efficient combustion of the fuel, which leads to a significant increase in power and torque compared to an equivalent aspirated engine.
Advantages of Turbo
The turbocharger offers a number of key advantages in modern engines:
1. Increased Power
The main advantage of the turbo is the significant increase in power. A turbocharged engine can produce much more power than a naturally aspirated engine of the same displacement. This makes it ideal for applications where extra power is required, such as motor racing and sports cars.
2. Improving Fuel Efficiency
Although turbocharging increases power, it can also improve fuel efficiency. Since compressed air allows better combustion of fuel, the engine can get more power from a given amount of fuel. This translates into better fuel efficiency.
3. Reducing Emissions
A turbocharged engine can reduce harmful gas emissions, as more efficient combustion means less fuel wastage and fewer harmful emissions.
4. Greater Torque
The turbocharger provides a significant increase in torque at lower revs. This means that the engine has a quicker response to acceleration, which results in a more dynamic drive.
5. Altitude Compensation
The turbocharger is particularly useful in high-altitude applications, such as aircraft. Since the air at high altitudes is less dense, the turbo can compress the air for optimal performance.
Turbo Challenges
Despite their many advantages, turbo engines present some challenges:
1. Turbo Lag
The main disadvantage of the turbocharger is so-called 'turbo lag'. This is the delay between the moment when the accelerator is pressed and the moment when the turbo starts to produce sufficient pressure. This is most noticeable at lower revs, when exhaust gas flow is restricted.
2. Greater Complexity
Turbo engines are more complex than naturally aspirated engines. They require additional components such as an intercooler and exhaust gas release valves.
3. Maintenance
Turbo engines require regular maintenance, such as oil changes and component cleaning. In addition, the turbo components themselves can wear out over time.
Conclusions
The turbocharger is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the automotive industry. It offers significant benefits in terms of power, efficiency and reduced emissions, but it is not without its challenges. Proper design and maintenance are essential to ensure optimal functioning of the turbo and the engine as a whole. Overall, the turbo is a key element in modern engines and will continue to play a central role in the evolution of the automotive industry.